
Block diagram of the ECG SoC [7] Download Scientific Diagram
The recording of the electrical activity associated with the functioning of the heart is known as Electrocardiogram. ECG is quasi-periodical, rhythmically repeating signal synchronized by the function of the heart; which acts as a generator of bioelectric events.

Block diagram of proposed ECG system. Download Scientific Diagram
The electrocardiogram (ECG) records from the body surface and registers the differences in electrical potential generated by the heart. The signal recorded is determined by action potentials generated by millions of individual cells and their sequence of activation. A multitude of factors, both cardiac and extracardiac, alter the final electrical signal. For instance, the electrical forces.
PPT Patient Monitor (Bedside Monitor) PowerPoint Presentation ID
This Osmosis High-Yield Note provides an overview of Electrocardiography essentials. All Osmosis Notes are clearly laid-out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. Find more information about Electrocardiography: ECG basics. ECG rate and rhythm.

ECG Basics Heart Blocks Diagnosis Cardiology MedStudent GrepMed
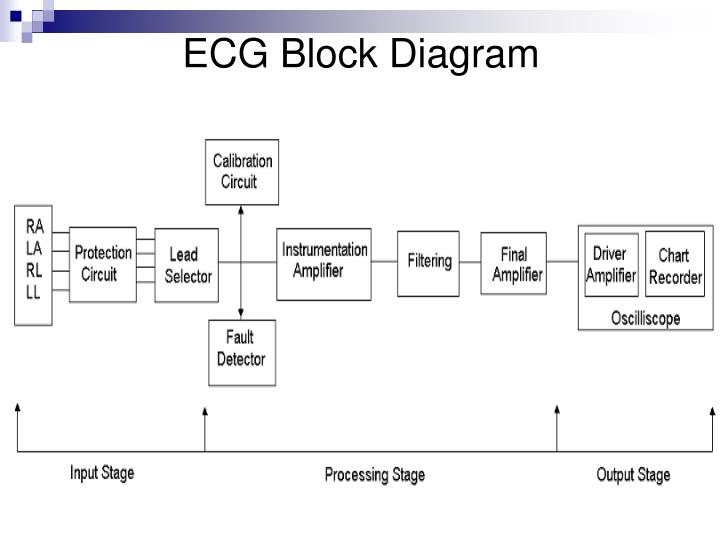
ECG Machine Block diagram and working: ECG Machine Block diagram Normally we use the above set up for the measurement and plotting of ECG. The main blocks of an ECG machine and the function of each block is explained below. 1. Electrodes: We know the ECG electrodes mainly used for the pickup of ECG are five in number.
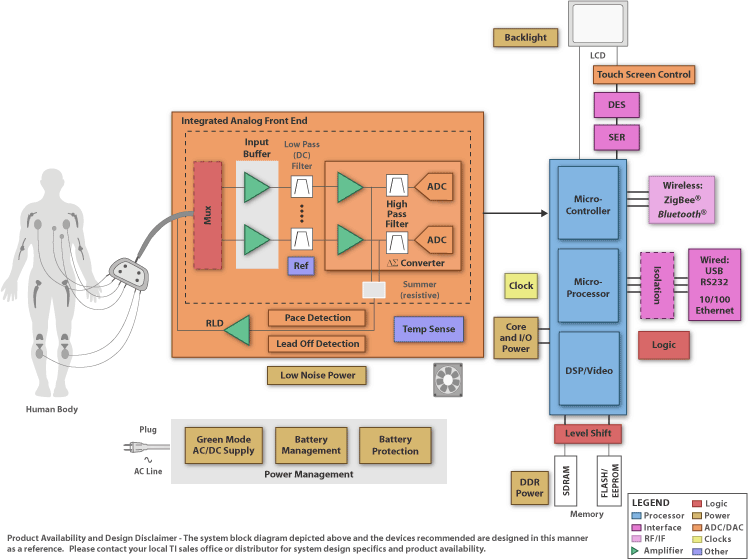
Block Diagrams Texas Instruments ECG Electroc... element14 Medical
Full-featured ECG functional block diagram. Features Understanding the required electronic components for an ECG is easier if it is separated into the analog front-end (AFE), which digitizes these signals, and "the rest of the system," which analyzes, displays, stores and transmits the data.
PPT Electrocardiographs ECG part 3 PowerPoint Presentation, free
Electrocardiography.ppt ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals Membrane potential membrane composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins Ion transporter/pump proteins actively push ions; ion channels allow ions to move. electrically equivalent to a set of batteries and resistors inserted in the membrane
Heart Block Dysrhythmias EKG Lesson 316
Many of the ECG rhythm strips come from the collection of the late Dr. Alan Lindsay, master teacher of electrocardiography. Most of the 12- and 6-lead ECGs were recorded at LDS Hospital in Salt Lake City, Utah. Marquette Electronics has also given permission to use ECG rhythms and diagrams from their educational posters.

The functional block diagram of ECG IC Download Scientific Diagram
Figure 2: Block diagram Above is a basic block diagram of our design. It features the main components that we must design to build a functional and portable ECG. Figure 3 below illustrates a criterion for programming capabilities within the structure of the design.
Clinical electrocardiography and ECG interpretation ECG interpretation
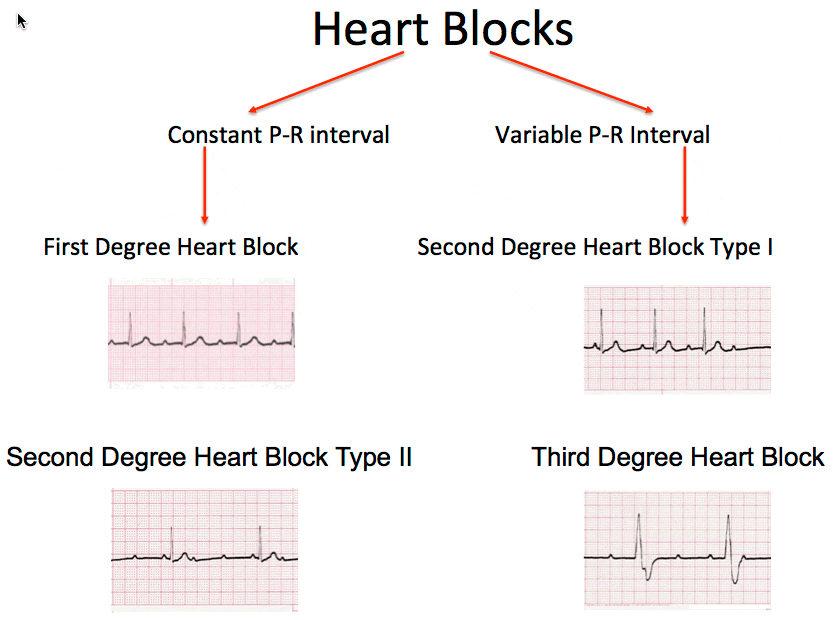
This chapter discusses third-degree AV block, which is synonymous with AV dissociation, complete AV block, AV block III and AV block 3. In third-degree AV block, no atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles. The atria and the ventricles are electrically dissociated from each other. This condition is referred to as atrioventricular (AV.

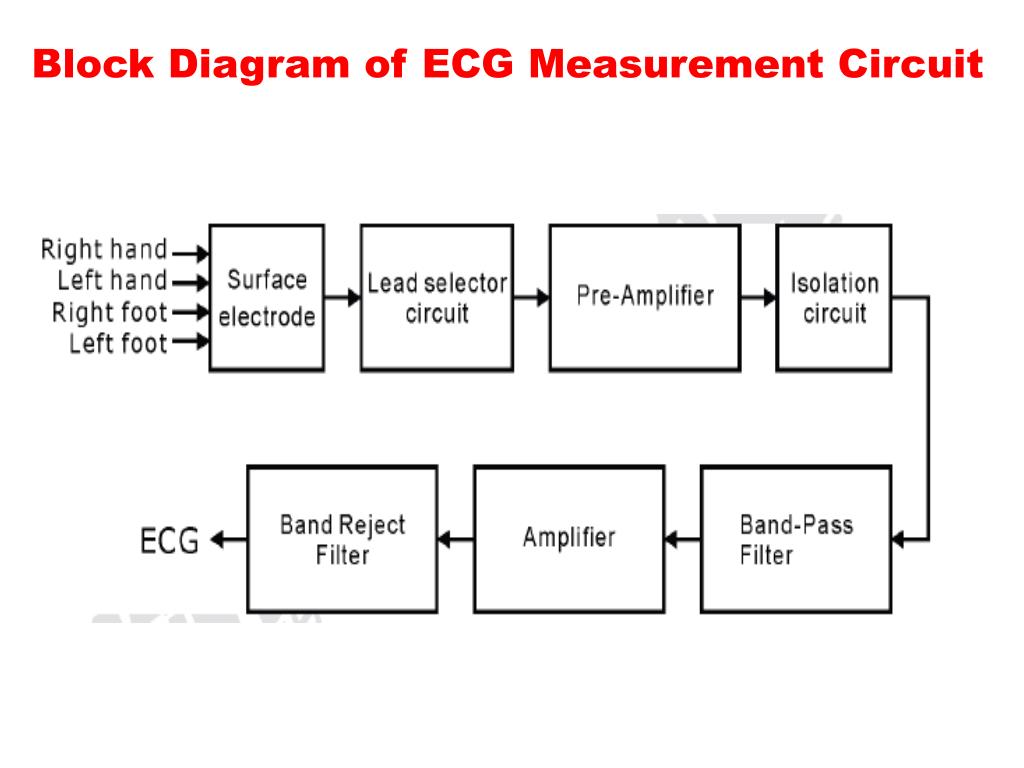
ECG circuit block diagram and analog circuit schematic. Since actual
1 st degree heart block 1st degree block indicates slowed transmission of electrical activity through the AV node - therefore giving a prolonged PR interval. It can be a normal variant. 2 nd degree heart block There are two varieties of 2nd degree heart block to be aware of: Mobitz type 1 (Wenckebach)

PowerPoint tutorial How to draw ECG block diagram in PowerPoint YouTube
The ECG demonstrates complete AV dissociation, with independent atrial and ventricular rates. Complete heart block: There is AV dissociation, with the atrial rate (~100 bpm) independent of the ventricular rate (~40 bpm) In complete heart block, there is complete absence of AV conduction, with none of the supraventricular impulses conducted to.

Shows block diagram of a basic single channel ECG machine. The dotted
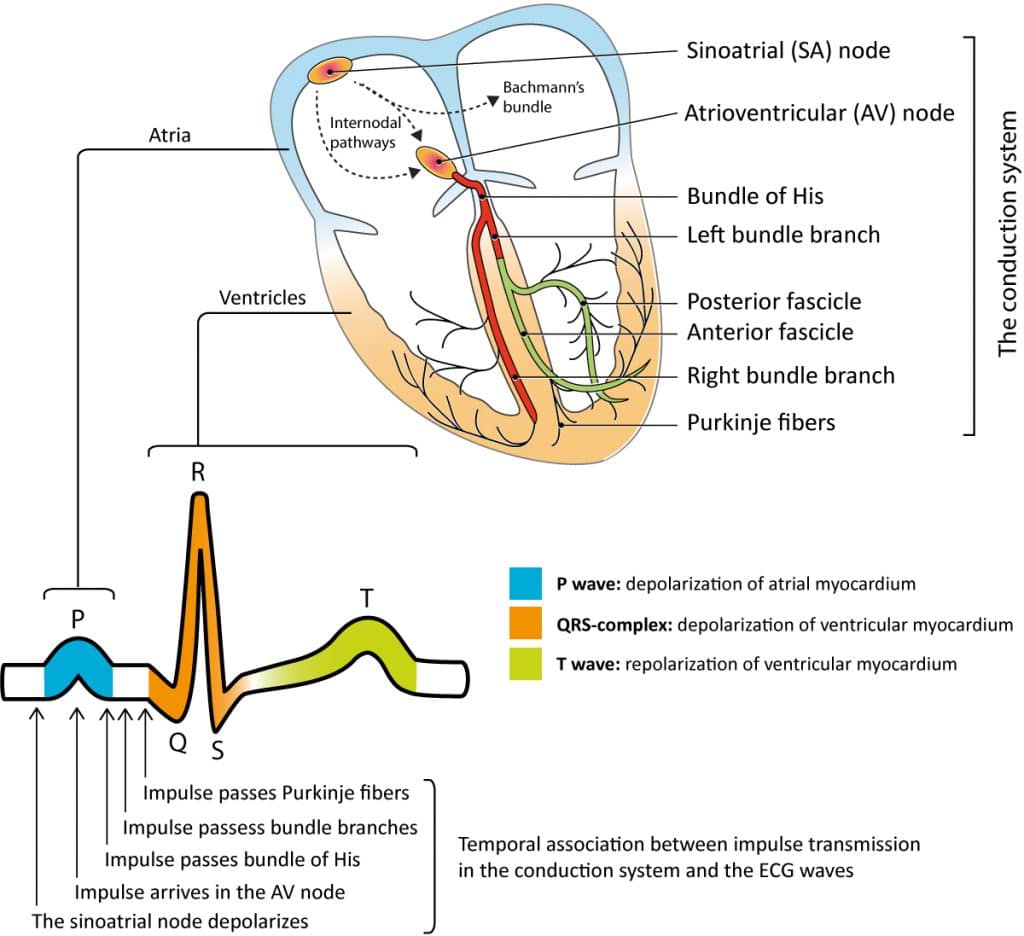
It is used to record the electrical activity of the heart from different angles to both identify and locate pathology. Electrodes are placed on different parts of a patient's limbs and chest to record the electrical activity. Parts of the ECG explained P waves P waves represent atrial depolarisation.

a) Block diagram and (b) photograph of ECG acquisition module
Section 1, Chapter 1 In Progress Cardiac electrophysiology and ECG interpretation Chapter contents Show Principles of cardiac electrophysiology and electrocardiography (ECG) To ensure effective cardiac pumping function, the atria and the ventricles must be activated rapidly and sequentially.

Shows block diagram of a basic single channel ECG machine. The dotted
Conduction Blocks First-degree block First-degree block PR interval >200 msec (1 large square) Second-degree block Mobitz Type I (Wenckebach Block): progressive prolongation of the PR interval before the missed QRS complex Mobitz Type II (Hay Block): absence of progressive prolongation of the PR interval before the missed QRS complex
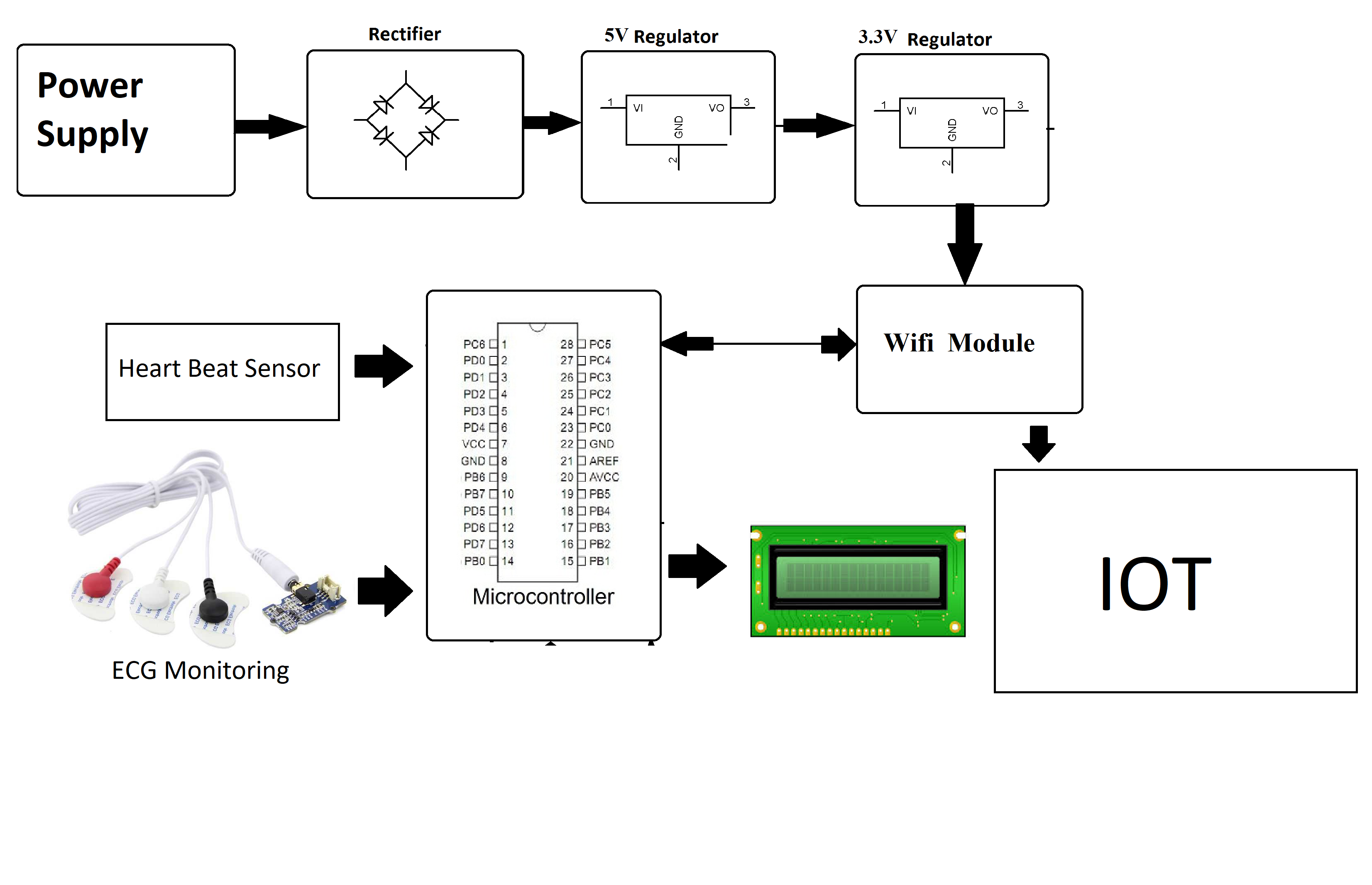
IOT Based Heart Defect Monitoring System Using ECG
This is seen in ECG 'A' below; ECG 'B' shows the treatment for 3rd degree AV block; i.e., a ventricular pacemaker. The location of the block may be in the AV junction or bilaterally in the bundle branches. AV Dissociation (independent rhythms in atria and ventricles) Not synonymous with 3rd degree AV block, although AV block is one of the causes.

Shows block diagram of a basic single channel ECG machine. The dotted
View the TI Electrocardiogram (ECG) block diagram, product recommendations, reference designs and start designing.